
A memorable HR journey, for employees to remember
HRIS
Manage your HR Information
Employee profiles, company directory, org-chart and more! We make it really easy for you to manage HR data with self-service options – on web or mobile – which ensure it’s always up-to-date.

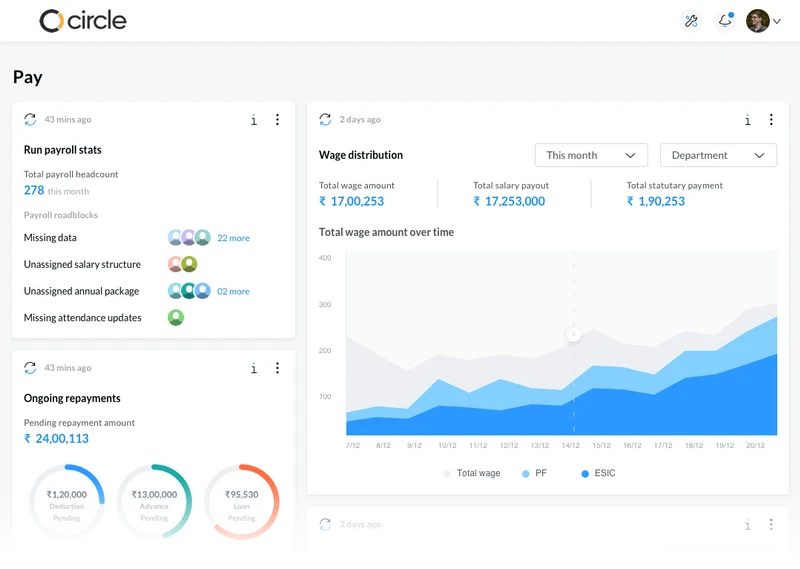
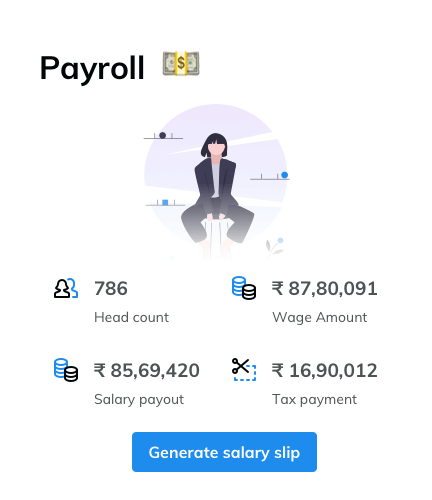
Payroll
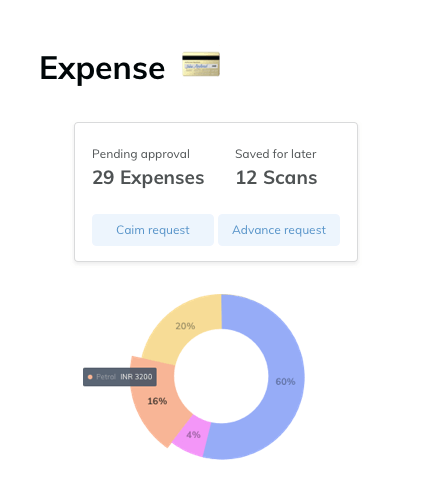
Automate payroll & expense claims
Make payroll stress-free with our robust and reliable processing engine which not only automates the calculations but also simplifies the complications, not just for you but for your employees too!
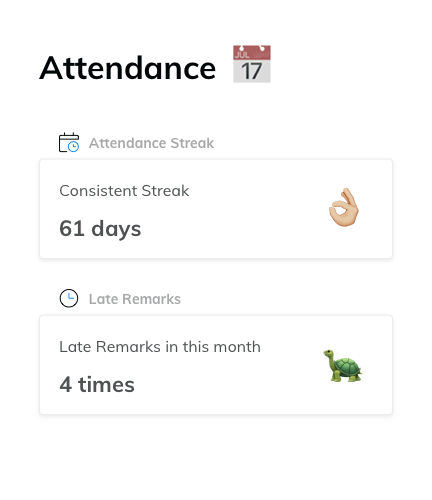
Attendance
Track attendance & time-off
Performance
Review performance & OKRs
Set ambitious objectives, define expected results and check-in to measure goals regularly. Design unique feedback forms, conduct 360° performance reviews and establish a fair appraisal system.
Operations
Organize HR operations
Put aside the paperwork and generate online HR letters from ready made templates, store important docs on the built-in HR drive, and optimize utilization of your IT assets with a smart inventory.
Onboarding
Streamine HR processes
Recruit (Coming soon)
Recruit candidates and make careers

HRIS
Manage your HR Information
Employee profiles, company directory, org-chart and more! We make it really easy for you to manage HR data with self-service options – on web or mobile – which ensure it’s always up-to-date.


Payroll
Automate payroll & expense claims
Make payroll stress-free with our robust and reliable processing engine which not only automates the calculations but also simplifies the complications, not just for you but for your employees too!


Attendance
Track attendance & time-off



Performance
Review performance & OKRs
Set ambitious objectives, define expected results and check-in to measure goals regularly. Design unique feedback forms, conduct 360° performance reviews and establish a fair appraisal system.


Operations
Organize HR operations
Put aside the paperwork and generate online HR letters from ready made templates, store important docs on the built-in HR drive, and optimize utilization of your IT assets with a smart inventory.

Onboarding
Streamine HR processes


Recruit (Coming soon)
Recruit candidates and make careers










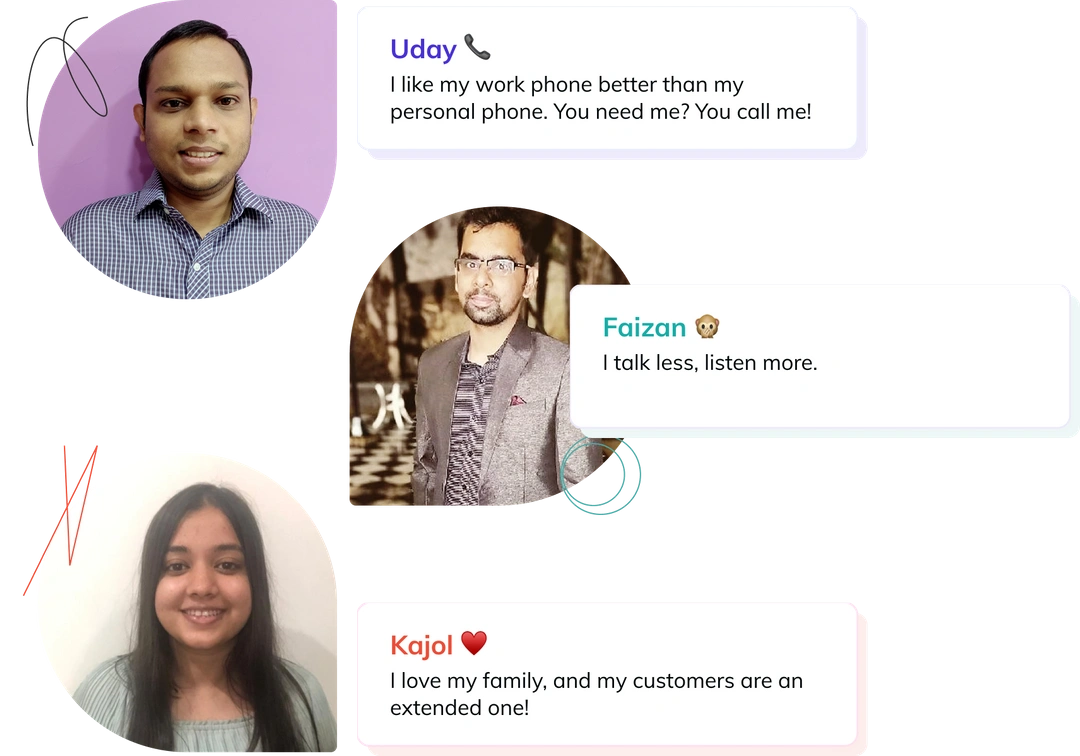
We are fast, fanatic and funny (we think) when it comes to supporting you. We believe that features will come and go, but it’s how we make you feel that matters the most.
Awarded 4 years in a row. Best rated HRMS in the market!




We have had a wonderful experience since the time we began working with sumHR. It's a convenient, accurate and a cost effective HRM system, with reliable and prompt support.
Swati Bhargava
Co-founder

I am a totally satisfied customer and very happy with the sumHR team. It's certainly the best HR software I've used until now. Their support response times are impressive, and the TAT on complex issues is great too.
Aastha Sharma
4PL Consultancy

Even after 5 years, it's a wonderful experience using sumHR and our relationship continues to strengthen every year. It's a convenient, accurate and a cost effective HRM system, with reliable and prompt support.
Deepali Raut
Chowgule Construction Chemicals


It's actually like sumHR has become a part of our company. They understand our needs and remain available whenever needed. Their promptness with support is commendable.
Shruthi Reddy Sheri
Worldview

Take your first step towards bringing happiness in your HR! Our customer team will guide you.